In the ever-changing world of online search, Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) emerges as a prominent player that demands attention, compelling SEOs and content marketers to reevaluate their strategies. This article delves deep into Google SGE, emphasizing its critical role in shaping the direction of search.
With its AI-generated responses, SGE takes the lead in the top section of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), creating a cloud of uncertainty within the SEO community. This leaves many pondering the potential impact on organic search visibility. Such a situation underscores the need for a strategic shift in content development that aligns with and appeals to SGE’s criteria.
While SGE is still in its beta phase and receiving ongoing updates, it’s evident that content teams must formulate SEO strategies tailored to Google Search Generative Experience. There are more viable choices than waiting on the sidelines until its formal introduction. This post serves two distinct purposes: it not only demonstrates the art of crafting content preferred by SGE but also offers insights into maintaining strong rankings and driving organic traffic amidst a constantly evolving search landscape. Let’s dissect the complexity and master a Google Search Generative Experience SEO plan that ensures exposure and relevance.
What Is Retrieval-Augmented Generation?
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) involves obtaining relevant documents or data based on a query and utilizing them as a prompt to fine-tune a language model’s output. This idea assists language models in becoming more grounded in reality and reduces the likelihood of generating inaccurate information.
While many people believe that Microsoft introduced this concept through Bing, it was actually first published by the Facebook AI Research team in May 2020 in their paper titled ‘Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks,’ which was presented at the NeurIPS conference. Neeva was the first to implement this concept in a major public search engine, resulting in impressive featured snippets.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) is a significant advancement because it enables language models to incorporate new information, thereby enhancing their output. This is particularly evident when using Bing Search or encouraging real-time crawling in a ChatGPT plugin like AIPRM.
Moreover, it represents the most effective means to ensure that language models generate more accurate content. As awareness of this approach grows, it is expected that more organizations and agencies will adopt it.
How Does Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Work?
As a student working on a research paper, you’ve already delved into numerous books and articles related to your topic, establishing a solid understanding of the subject matter. However, to reinforce your arguments, you require specific data. This is where RAG comes to your aid as a valuable research assistant.
You simply provide it with a prompt, and it scours its extensive knowledge base for the most pertinent facts. This information can then be integrated into your content, enhancing its depth, aligning with your preferred style, and making it more engaging. Unlike Large Language Models (LLMs) that offer broad responses based on probabilities, RAG provides precise answers that can be traced back to their sources.
A RAG configuration comprises three crucial components:
- Input Encoder: The RAG system initiates with the Input Encoder, which transforms the input prompt you provide into a sequence of vector embeddings. These embeddings play a vital role in subsequent steps to accurately convey and interpret your request.
- Neural Retriever: This component is responsible for retrieving relevant contents from an external knowledge base based on the encoded input prompt. It operates like a search engine, sifting through vast amounts of content to identify the most pertinent sections or information to enhance your query. This stage is pivotal for acquiring the exact information needed for your task.
- Output Generator: The Output Generator blends the encoded input prompt with the retrieved documents to produce the final text output. This output aims to be comprehensive, contextually accurate, and engaging. It’s where the system assembles and presents the information logically, making it usable for your objectives.
To contextualize this, consider ChatGPT’s Bing implementation. When you interact with it, it takes your question, searches for papers, appends the most relevant portions to your prompt, and then returns the result.
For natural language processing tasks, all three components typically rely on pre-trained Transformers, a potent type of neural network. Google’s Transformer advancements are now widely adopted in the realm of natural language processing (NLP).
The Input Encoder and Output Generator are fine-tuned for specific purposes like question answering and summarization. In contrast, the Neural Retriever is often not fine-tuned but can benefit from pre-training on a substantial corpus of text and code to enhance its document retrieval capabilities.
RAG often operates in conjunction with document vector indexes or knowledge graphs. Knowledge graphs (KGs) are frequently employed because they effectively distill additional content into key facts.
The synergy between KGs and LLMs is a mutually beneficial arrangement that unlocks the potential of both. With many products relying on KGs, it’s high time to consider knowledge graphs as more than a mere curiosity or data source, recognizing their significance in Google’s growth and beyond.
The Drawbacks Of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
The advantages of RAG are readily apparent. It automates and enhances the language model’s understanding, resulting in improved output. However, let’s delve into some of the less obvious drawbacks:
Retrieval is Crucial:
The retrieval of relevant information plays a pivotal role in the RAG (Recovery-Augmented Generation) paradigm. Incorrect retrieval is equivalent to receiving a flawed order, leading to a decrease in output quality. The adage “garbage in, garbage out” underscores the direct impact of input data quality on output.
Data is Key:
RAG’s effectiveness strongly hinges on the accuracy of the data it utilizes. Outdated or insufficient data constrains the system’s capabilities. To achieve optimal results, ensure that the data it accesses is both current and relevant.
Beware of Echo Chambers:
When using RAG to generate content, it’s essential to prevent redundancy. If the retrieved documents contain repetitive information, the model may produce content that is repetitious or unoriginal. This can be problematic, especially in industries where uniqueness is a priority, such as SEO.
Prompt Length Limitations:
RAG models have limitations on the length of input or prompts they can handle. Some models, like Anthropic’s Claude, permit longer inputs, while many have restrictions. It’s crucial to be mindful of these constraints when using the model, as exceeding them may result in incomplete or erroneous outputs.
Staying on Script:
Even with careful retrieval, RAG models can produce text that deviates from the intended script. This means that you must exercise caution and review the output to ensure it aligns with your requirements. Such issues may have contributed to Google’s initial hesitancy in adopting this technology.
What Is SGE And What Does It Mean For Your Website
Google’s Search Labs’ Search Generative Experience (SGE) is essentially an AI experiment designed to anticipate and respond to a user’s search query directly on the homepage of search engine result pages (SERPs).
When you perform a search on Google, SGE takes precedence, presenting an AI-generated snapshot of critical information as the primary result. Upon selecting the top result, Google provides additional responses below, including more connected webpages, product links, descriptions, and other relevant information.
What makes it unique is its conversational feature, enabling users to pose follow-up questions. This capability adds context to their initial requests, resulting in more informed and personalized results.
SEO services are increasingly focusing on implementing strategies tailored for Google’s Search Generative Experience SEO, recognizing its growing impact on search rankings and visibility. These specialized services aim to optimize content, keywords, and user engagement metrics to align with the unique criteria set by Search Generative Experience, ensuring that businesses stay competitive in this evolving search landscape.
Understanding The Google Search Generative Experience Landscape
SGE Real Estate: A Distinctive Presence In The SERP Landscape
SGE real estate is set to diverge from the current Search Engine Results Page (SERP) landscape. While an SGE summary bears a resemblance to other SERP components, like a highlighted snippet, it occupies significantly more screen real estate. In numerous queries, these auto-generated summaries often span the entire desktop screen, necessitating mobile users to scroll extensively.
However, the standard search functionality and advertisements continue to occupy a substantial portion of the screen. We’re not entirely convinced that Google will reduce its advertising display, but it seems to be the prevailing trend. The addition of advertisements, whether placed before or after the AI summary, will unquestionably further diminish the visibility of organic results, exacerbating the current situation.
Google recently altered the layout of SGE-generated summaries. They no longer dominate the entire above-the-fold area and do not display any linked source images; instead, they offer a concise preview and a “Show more” button. In comparison to the previous arrangement, the impact on organic traffic is expected to be minimal.
Let’s examine the AI snapshot for “net banking risk” on two distinct dates:
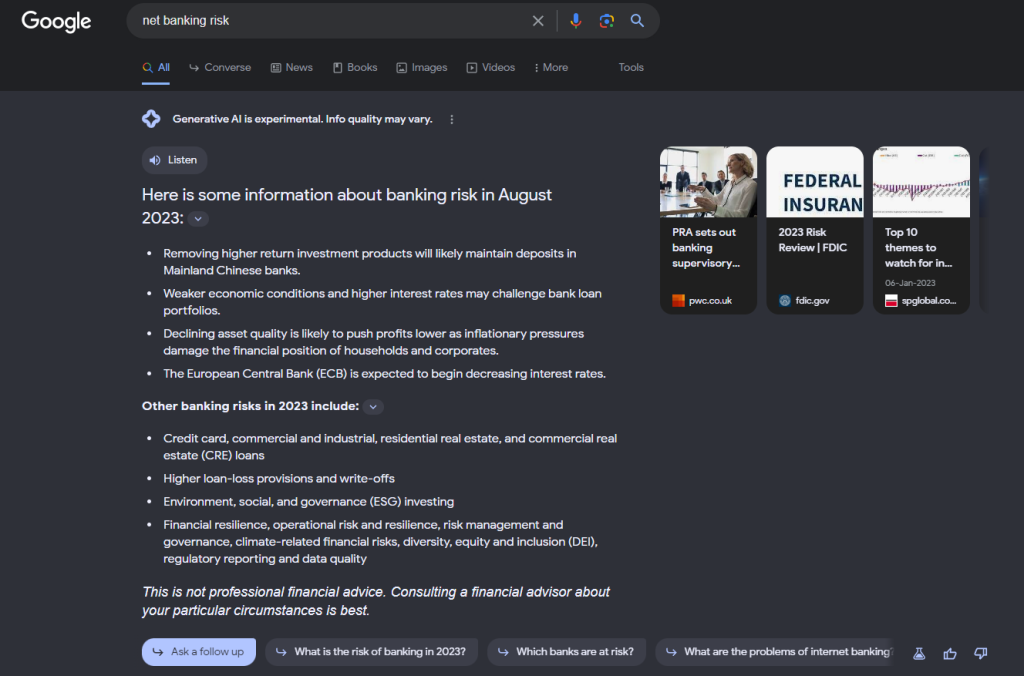
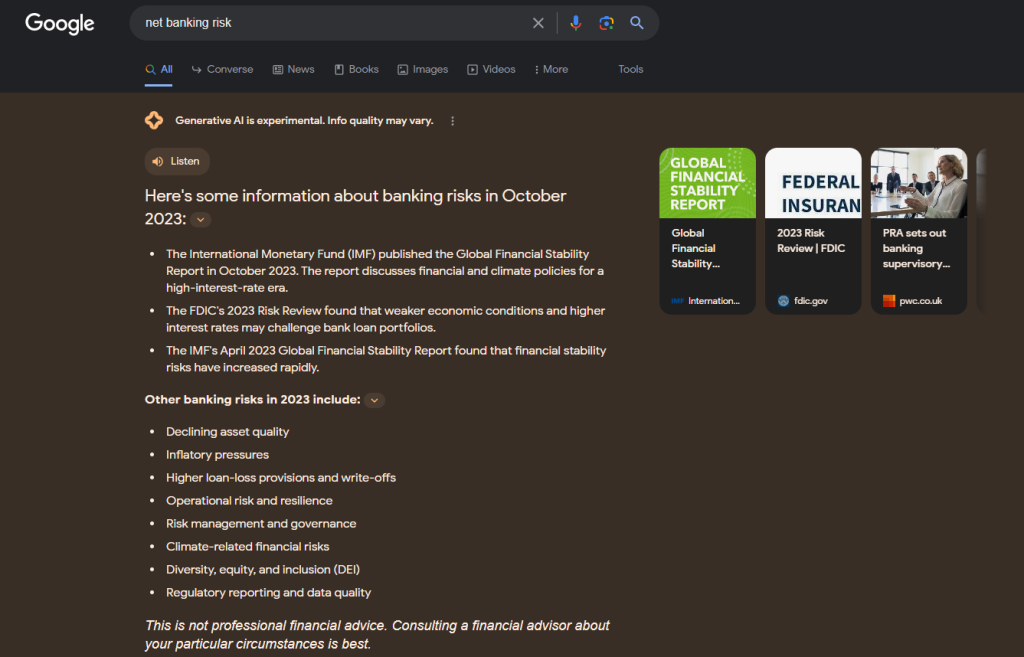
Towards the end of September, the overview stood at approximately 780 pixels in height. However, the most recent one from early October is notably smaller, measuring only about 230 pixels – not even a third of the original size.
This alteration in layout could potentially lead to a reduced impact on organic traffic when compared to the earlier version.
The Influence Of AI Overview Layouts: From Click-Through Rates To Organic Results
Images associated with the mentioned sources are likely to influence click-through rates (CTR). Visually engaging graphics, such as enticing YouTube thumbnails, generally yield higher CTRs compared to less captivating ones. This has repercussions for the cited sources, as it’s not just about having an image displayed; it’s about making it appealing to users, thereby giving you an opportunity to stand out.
The availability of an AI summary may lead to a decline in CTRs for regular organic results. This is a natural outcome since any content appearing above the fold holds more significance for websites and search results, as with any SERP that features multiple elements; the appearance and positioning of these elements significantly affect CTR.
Current Status And Trends In SGE: Ads, Layouts, And Ever-Changing Dynamics
In SGE, there are now fewer advertisements than in regular search results. This reduction comes as a result of extensive experimentation and research, drawing insights from Moz and Insight Partners. The number of advertisements in SGE may vary as Google experiments with different layouts. However, they exercise caution to ensure that their search ad revenue remains intact.
SGE is in a constant state of flux. Late in August, SGE announced its commitment to addressing customer concerns regarding information sources, but that’s not the only change. Here are some observations we’ve made after months of monitoring SGE:
- Queries Triggering Overview: The types of queries that trigger an SGE overview are evolving, with some on the rise and others on the decline.
- E-commerce Keywords: E-commerce category keywords no longer automatically generate an SGE summary, indicating a shift in the types of queries that activate this feature.
- YMYL Queries and Trust: SGE overviews are increasingly being provided for YMYL inquiries (Your Money or Your Life). This suggests that Google is gaining confidence in the accuracy of SGE’s information in critical areas.
- Local Pack Variations: Local packs, which display local business results, come in various combinations, ranging from two to five packs, with five packs being the most common.
- Increasing Ad Volume: According to studies and research, there’s a modest uptick in the number of ads within SGE. This might have an impact on the overall user experience and the visibility of organic results.
- Ad Placement Above Overview: Advertisements are more frequently placed above the SGE summary, potentially affecting user engagement and click-through rates.
- Dynamic Overview Size: The size of the SGE summary for the same query varies over time. This dynamic aspect can influence how users interact with the displayed information.
- SGE Response Layouts: SGE features a variety of response layouts, indicating ongoing research or adaptation to user behavior.
- Changing Overview Content: The content of the SGE overview undergoes regular changes, showcasing the dynamic nature of the feature and its adaptability to evolving information.
In summary, these observations underscore the dynamic and evolving nature of SGE, highlighting changes in trigger queries, the treatment of e-commerce keywords, increased trust in specific query types, variations in local packs, the increasing number of ads, shifts in ad placement, fluctuating overview sizes, diverse response layouts, and dynamic content alterations. These elements emphasize the complexities and continuous transformations in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP) ecosystem.
What Remains Unknown About SGE
Let’s delve into the unanswered questions surrounding SGE.
- Will SGE’s Instability Persist?
First and foremost, is this level of volatility the new norm for SGE? AI trends shift rapidly, and the alterations are frequently substantial. Consider these examples, only two weeks apart:
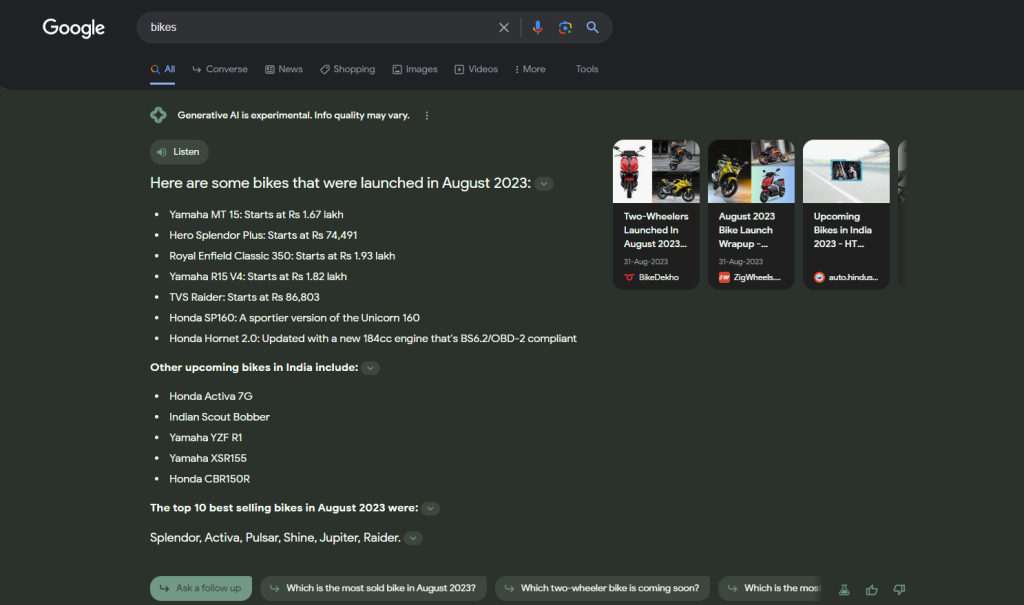
In late August 2023, a search for “bikes” revealed a prominent SGE response dominating a significant portion above the fold. You could expand it by clicking “Show more.”
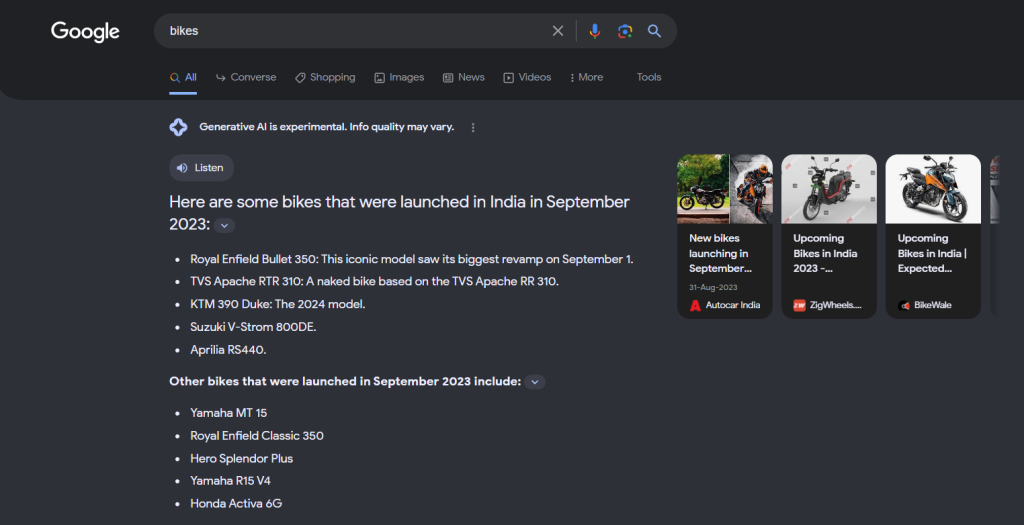
Fast forward to mid-September 2023, and the SERP for “bikes” displays a noticeable shift. The SGE response has doubled in size compared to the previous snapshot, occupying an even more substantial chunk.
If your website missed the first update, the impact of the second one could be more than twice as significant. The challenge lies in predicting whether this volatility will become a permanent feature of SGE. Providing precise estimates is difficult, especially given the potential for Google to alter its layout.
- Will Official SGE Data Ever Surface?
This poses a significant issue with far-reaching consequences. While the SEO community will likely come up with methods to track SGE changes over time, the release of official data may be delayed. For instance, Microsoft promised to integrate Bing Chat data into Bing Webmaster Tools, but the actual implementation was disappointing.
Data from both websites and conversations were mixed without any filtering tools, rendering the data essentially useless. It may take many months for official SGE statistics to appear in the Google Search Console.
Despite the absence of official data, we maintain optimism that SEO tool providers and knowledgeable community members will discover ways to gain insights into SGE. This process, however, will require time.
Also Read: Top 18 Paid SEO Tools That Are Worth The Money in 2025
- Anticipating CTR in the AI Overview
So, how can one secure a place in the AI overview? The answer to this is still evolving. From our observations, a reverse-engineering approach can be beneficial, especially for informational queries. Analyze the content and perspective of the overview, then present equivalent information as clearly as possible. Keep in mind that SGE elements vary, including perspectives, responses to similar queries, and sources.
When it comes to click-through rates (CTR) in the AI overview, it’s a bit tricky. If every query generates a snippet with similar attributes, the CTR may be lower than for featured snippets. However, this can’t be generalized. It’s reasonable to expect a lower CTR than the current top rankings for informational queries, where CTR typically falls in the range of 25-30%.
- Key Considerations to Keep in Mind for Search Generative Experience SEO Preparation
Now, let’s delve into the crucial aspects to avoid when preparing for SGE. Whether you’re an SEO firm, a freelancer, or a corporation, steering clear of the following pitfalls is essential:
- High Volatility: SGE is known for its extreme volatility.
- Scalability Concerns: The ability to scale within any framework is currently questioned.
- Lack of Official Data: Official data is lacking, and it’s unclear how users will interact with the new features.
To illustrate the volatility, consider an experiment where two individuals, using the same VPN, conducted simultaneous searches for the same query. Out of 60 observations, the average source overlap was just 57%, and variations in content were prevalent. This underscores the unpredictable nature of SGE.
Differences
- Small differences involve minor text tweaks and slight layout adjustments.
- Medium variations entail textual changes along with slight modifications to the layout.
- Big differences refer to substantial text alterations combined with significant changes to the layout.
Consider the following query: “Pros and Cons of Electric Vehicles.”
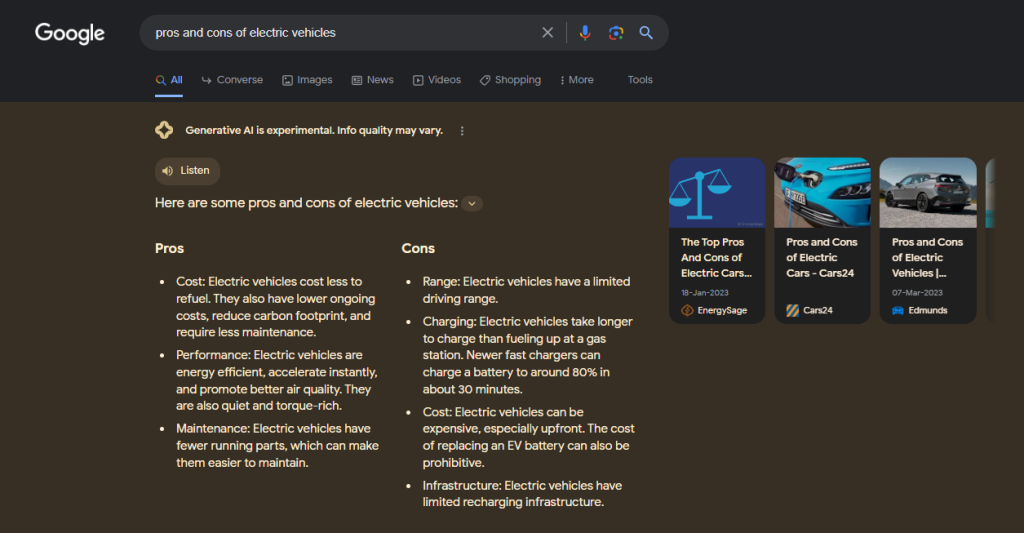
In the first scenario (User A), the screenshot displays a Search Engine Results Page (SERP) featuring a “Show more” option for the SGE response. Surprisingly, no drawbacks are readily apparent.
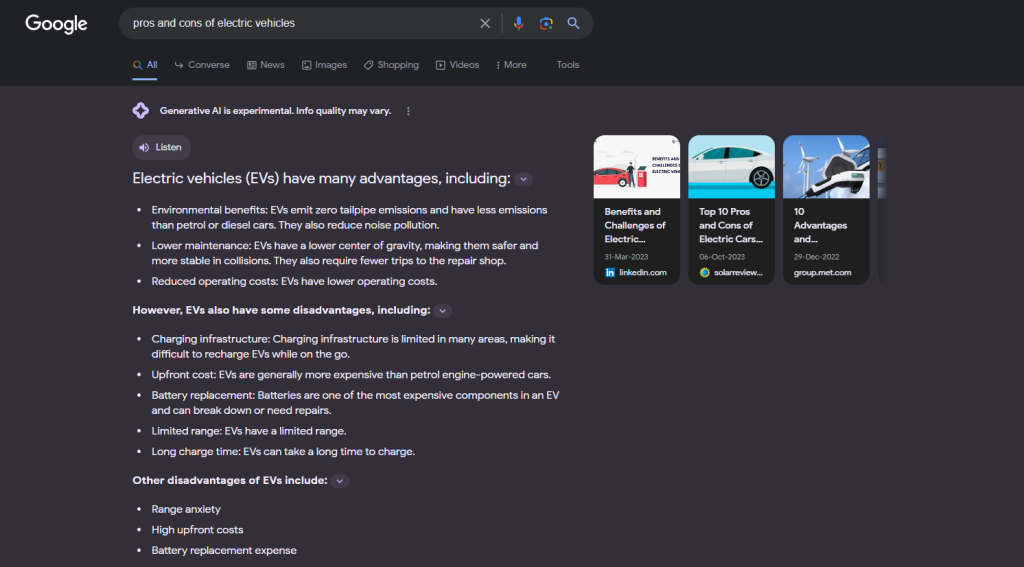
In the second case (User B), another SERP snapshot reveals a differently styled SGE response, presenting both positives and negatives in a readily displayed format.
In summary, dedicating a significant amount of time and resources to developing models and frameworks for predicting traffic fluctuations may not yield substantial benefits. SGE will likely have an impact, especially on organizations providing information.
However, the exact magnitude of this impact remains uncertain, and attempting to anticipate it with estimates ranging from -95% to +200% is ineffective. SEO professionals will need to continuously test and adapt their strategies until Google provides more specific information.
How Google’s Search Generation Experience Works (REALM, RETRO, and RARR)
In the market, many people believe that Google developed SGE in early 2023 in response to Bing. However, in their article “Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training (REALM),” released in August 2020, the Google Research team first introduced the idea of RAG.
This paper presents a strategy for “open-book” question answering that involves leveraging a corpus of documents with a language model and employing the masked language model (MLM) methodology popularized by BERT. REALM’s role is to recognize complete documents, determine the most relevant sections within them, and then return the single most pertinent paragraph for information extraction.
During the pre-training phase, REALM is taught to predict masked tokens in a sentence, but it also learns to retrieve relevant documents from a corpus and incorporate them into predictions. Compared to typical language models, REALM’s unique methodology allows it to generate more accurate and informative content.
The DeepMind team at Google took this concept further with the Retrieval-Enhanced Transformer (RETRO). RETRO shares similarities with REALM but employs a different attention mechanism. It adopts a more hierarchical approach to attending to the retrieved documents, resulting in more coherent and fluid writing than REALM.
Following RETRO, the teams developed Retrofit Attribution Using Research and Revision (RARR), a method distinct from traditional language modeling. RARR doesn’t generate text from scratch; instead, it extracts a group of candidate passages from a corpus and ranks them to determine the most suitable one. This approach allows RARR to produce more accurate and informative text, but it is computationally intensive.
Each of these three RAG variants has its unique advantages and disadvantages. Although what is actually in use is likely a combination of these advancements and others, the fundamental concept remains consistent: documents and knowledge graphs are searched and used in conjunction with a language model to generate a response.
According to publicly available information, SGE combines the PaLM 2 and Multitask Unified Model (MuM) language models with elements of Google Search as its retriever. This implies that Google’s document index, as well as Knowledge Vault, can be used to fine-tune the responses.
Despite Google’s dominance in the search market, Bing was the first to leverage this information retrieval and personalization paradigm.
The Perils of Search Generative Experience
Google’s purpose is straightforward: to organize and make the world’s information available. When we look ahead, the usual ten blue links may become as outdated as MiniDiscs and two-way pagers. The way we search now is merely a stopgap on the road to something better.
ChatGPT has introduced multimodal features mimicking the type of computer shown in “Star Trek,” a concept Google developers have discussed. People don’t want to sift through possibilities; they desire solutions.
A recent opinion piece titled “Situating Search” argues that consumers do not want to engage in extensive research or authenticate content. Instead, search engines have accelerated.
As a result, here’s what is likely to occur.
Changes in Search Behavior:
Individuals are increasingly using longer, more detailed queries as they move away from using short, popular search phrases. This is because they realize that Google is becoming more proficient at understanding natural language. Consequently, consumers prefer more descriptive middle and long-tail search keywords rather than using just a few words, causing shorter head terms to lose popularity.
Shifts in Click-Through Rates (CTR):
The traditional ten-blue links are experiencing a decrease in clicks due to AI-generated snapshots, reducing the visibility of regular organic search results. The once-impressive click-through rate of 30-45% for Position 1 is expected to decline significantly. However, the figure below is for illustrative purposes only since we currently lack precise evidence to predict how this transition will unfold.
Increasing Complexity in Rank Tracking:
For some time, rank-tracking systems have coped with the rendering of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) with varying characteristics. However, these tools are now required to wait longer for each query. This is particularly crucial because most Software as a Service (SaaS) applications rely on platforms like Amazon Web Service (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure, which charge by the hour. Whereas displayed results might have previously taken 1-2 seconds to return, they may now take significantly longer, resulting in additional expenses for rank tracking.
Enhanced Personalization through Context Windows:
Including follow-up questions in search interactions offers users a “Choose Your Own Adventure”-style journey. As the context window narrows, highly relevant content tailored to each user’s specific needs, rather than generic results, is presented. This shift broadens the scope of searches. Content creators must now ensure that their content is adaptable enough to appeal to various stages of the user experience while staying within the consideration set.
Evaluating Your SGE Security Risk
We currently lack information about modifications to user behavior in the SGE environment. If you have any such information, please reach out to us.
However, we do possess historical insights into search user behavior. Our research indicates that, on average, consumers take 14.66 seconds to make decisions about search results. This implies that a user will not wait for more than 14.6 seconds for an automatically generated AI snapshot. Therefore, any processing time exceeding this threshold doesn’t pose an immediate threat to your organic search traffic, as users are likely to scroll down to the regular results instead of waiting.
Furthermore, historically, when highlighted snippets appear in the SERPs, they account for 35.1% of clicks.
These two data points can be used to make several assumptions for building a model to estimate potential traffic loss from this rollout.
Let’s start by reviewing the current state of SGE using the available data.
The Present State of SGE
Now, let’s delve into the current issue with SGE. We’ve faced a data shortage, and it would be beneficial to bridge that gap. Fortunately, we recently uncovered a dataset in SGE containing over 91,000 inquiries and their corresponding SERPs. For each of these queries, we have vital information, including:
- The search query itself.
- The initial HTML when the SERP first loads.
- The final HTML after the AI snapshot loads.
- The time it takes for the AI snapshot to load.
- Whether the snapshot triggers automatically or requires a click on the “Generate” button.
- The type of AI snapshot – informational, shopping, or local.
- A list of follow-up questions.
- URLs in the carousel that appear in the AI snapshot.
- The top 10 organic results to assess any overlap.
- Snapshot status – indicating whether there’s a snapshot or a “Generate” button.
- “Show more” status – revealing whether the snapshot needs a user to click “Show more.”
Assessing Your SGE Risk Level
In the corporate world, the scarcity of data should never hinder your ability to assess potential risks. Many companies are eager to understand the potential traffic loss that might occur with the widespread availability of SGE (assuming this refers to some technology or service).
To address this, we’ve developed a model to estimate potential traffic loss. The core equation is straightforward:
Traffic Loss = Search Volume x CTR Difference
This calculation is applied explicitly to terms that involve an AI snapshot. The formula is more accurately represented as follows:
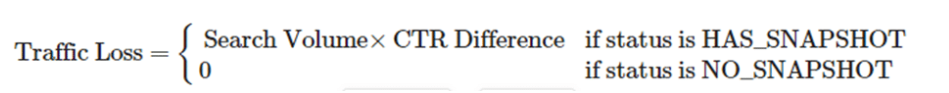
The true magic lies in the concept of Adjusted CTR, and achieving this involves some good old-fashioned number crunching. We need to thoroughly analyze how the SERP (Search Engine Results Page) appears in various scenarios, considering factors like page type, automatic triggers, and the “Show more” button.
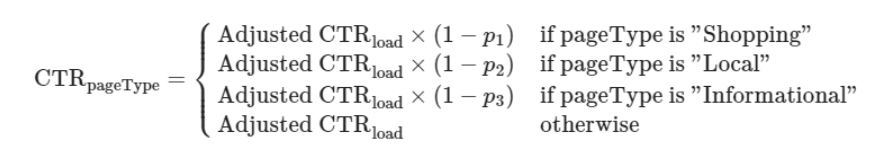
We calculate an adjusted CTR for each keyword, depending on whether an AI snapshot is present and the time it takes to load. The highest potential risk lies in shopping results, as they provide a full-page experience.
Several parameters influence our adjusted CTR calculation, which is then incorporated into a distribution factor.

In the context of the AI snapshot, this distribution factor demonstrates the weighted influence of carousel links, citation links, shopping links, and local links. Its value varies based on the presence or absence of these components, helping us determine whether any of these components are representative of the target domain.

To compile reports for non-client scenarios, we utilize vertical-specific CTR data from Advanced Web Ranking’s CTR research and non-branded keywords with nonzero traffic percentages from Semrush.
For our clients, we follow a similar procedure, but we take into account all terms that account for 80% of clicks, based on their customized CTR model obtained from Google Search Console.
Crafting An Search Generative Experience-adapted SEO Strategy
We have outlined some key elements to consider when refining your website’s Search Generative Experience SEO strategy.
These techniques are primarily based on our experience with eCommerce clients. However, most of the ideas we will share are applicable across various sectors. If you’re interested, we are always willing to develop a customized plan for your specific sector if you contact us.
Keyword Research Evolution
It’s time to shift our focus away from traditional, keyword-centric techniques and instead place more emphasis on user intent and topical relevance in our content production process. Given the changing landscape and the decreasing effectiveness of relying solely on keyword research, especially due to zero-click updates, this shift is particularly important.
Consider incorporating real-time query analysis tools, such as Google’s “People Also Ask” feature, to stay ahead. These tools offer valuable insights into current search patterns, enabling you to tailor your content to what visitors are actively seeking.
So, if your previous keyword research tools are falling short or providing outdated data, shift your focus towards understanding user intent and staying updated on real-time search trends. This strategic move ensures that your content remains current and impactful in the ever-changing digital landscape.
Also Read: Get Ahead in the Game: The Top 22 Free Keyword Research Tools for 2025
Enhancing Information Gain
Instead of fixating on word count, let’s adopt a systematic approach to ensure search visibility and success in rankings. Let’s delve into it.
When discussing competitive parity, the emphasis is on creating content that aligns with the search intent of the target keyword topic. Ensure that it provides the type of information that Google currently seeks for that specific term. For example, when creating a cybersecurity recommendations piece for customers, examine top-ranking content. Google prefers articles that explain the problem and offer actionable advice, without the need for a lengthy history lesson on cybersecurity.
In terms of information value, it relates to a patent Google filed in 2018. When ranking pages, it takes into account the uniqueness of the content. Always remember the insights gained while studying word count and analyzing competitors’ content. Using this as a foundation enables you to consistently provide value to your readers, enhancing overall content quality and increasing your chances of ranking well.
These concepts align seamlessly with Google’s user-friendly content approach, which rewards high-quality content that caters to readers while delivering genuine value. It significantly influences how well content ranks in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). Consistently offering fresh, valuable, and unique content on the SERP is crucial. Employ strategies to discover and cover fresh perspectives, viewpoints, and facts within your content. This approach ensures that your content remains relevant and improves its position in search engines.
Improving Content Readability And Directness
Notice how Google highlights the text it “reads” in purple when you interact with a website. This is made possible by Google’s Semantic Google Extractor (SGE), which prioritizes the extracted content from the source page. To effectively communicate with Google, it’s essential to employ semantic similarity, enabling the search engine to grasp the essence of your content.
To ensure that Google can easily reference your information, opt for simplicity over using complex or flowery language. Prioritize clarity and directness. Here are some tips for enhancing the readability of your content:
- Provide Direct Answers: Structure your content to offer straightforward and easily understandable answers to potential questions. This not only benefits users but also assists Google in extracting valuable information.
- Clear Headings: Utilize concise and descriptive headers that accurately convey the content that follows. Clear headings not only facilitate user navigation but also assist Google in understanding your page’s structure.
- Comprehensive FAQs: Incorporate Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on a wide range of important topics. This not only resolves user queries but also enhances the comprehensiveness of your content, increasing its chances of being cited.
Remember, the primary goal is to enhance the ease with which Google comprehends and extracts information from your website. The more concise and well-organized your content, the more likely it is to be acknowledged by Google.
Optimizing for Featured Snippets and SGE Citations
SGE, or whatever platform you’re using, prioritizes crediting the sources from which it gathers information. This is akin to a proper citation system in academic writing, ensuring accurate attribution.
Here’s an intriguing observation: when Google conducts a search and encounters a highlighted snippet, it seems to favor incorporating that snippet into its SGE response. It’s almost as if Google is saying, “Hey, this snippet contains valuable information; let’s include it in our comprehensive answer.”
So, if you wish to stand out in an SGE response, you can employ a creative strategy—essentially, do what individuals do to get a highlighted snippet.
Here are some steps to consider:
- Keyword Research: Start by searching Google for your main keyword. Look for any featured snippets related to it.
- Analyze the Format and Content: Scrutinize the highlighted passage closely. Is it presented as a series of paragraphs or a neat list? Are there any bold elements? Visit the page selected by Google and determine the location of the highlighted content. Does it have an attention-grabbing H2 heading?
- Brainstorm Improvements: Put on your thinking cap. How can you enhance your data? Can you elucidate your argument more effectively? Are there opportunities to provide more specific steps? Perhaps your table needs a bit more detail?
- Optimize Your Content: Don’t forget what you discovered while working on your content. Emulate the style of the highlighted snippet. If it was a well-structured list derived from H3 headers, organize your content similarly.
Why go through all this effort? Well, highlighted snippets appear for various queries, but not for everyone. So, if a highlighted snippet doesn’t appear, how can you maintain a high rank and maximize the likelihood of SGE mentioning your page?
Capturing highlighted snippets and then adapting your content’s structure to align with existing snippets for your desired keywords is where these strategies come into play. It’s akin to giving yourself a better chance to shine even when the spotlight isn’t directly on you.
Encouraging Third-Party Mentions And Reviews
While we may not be overjoyed, the truth is that Google’s Search Engine (SGE) tends to favor pages that appear frequently. When a consumer searches for a product recommendation, a page that appears on eight separate top-ranking pages has a better chance than one that rarely appears.
In the future, the frequency with which other sources link to your page will become even more critical. Google places a significant emphasis on accumulating recommendations.
Now, let’s discuss strategy. How can you ensure that your page receives these endorsements? Start by increasing the number of third-party reviews. Encourage clients to share their experiences on platforms such as G2 and Capterra. Consider collaborating with other companies in your industry for co-marketing opportunities. Don’t forget to secure press coverage.
Google’s SGE is highly focused on prioritizing pages that consistently receive attention. So, ensure your page is being discussed, cited, and recommended on those high-ranking pages and trusted platforms, not just visible.
Crafting Opinionated Content
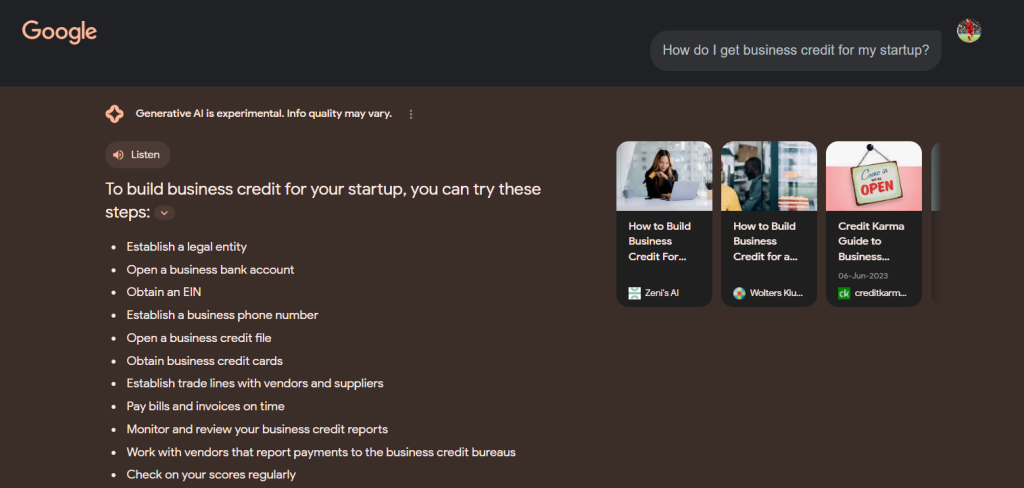
Google is revolutionizing the search game by cutting out the middleman. Certain keywords hold more value for businesses than others. When it comes to simple inquiries, AI-generated responses excel, providing concise and accurate answers in just a few pages.
Consequently, customers are veering away from direct website access since their queries find succinct responses. Take Google’s SGE, for example, which excels at addressing basic questions like “What is accounting?” and aggregating relevant information.
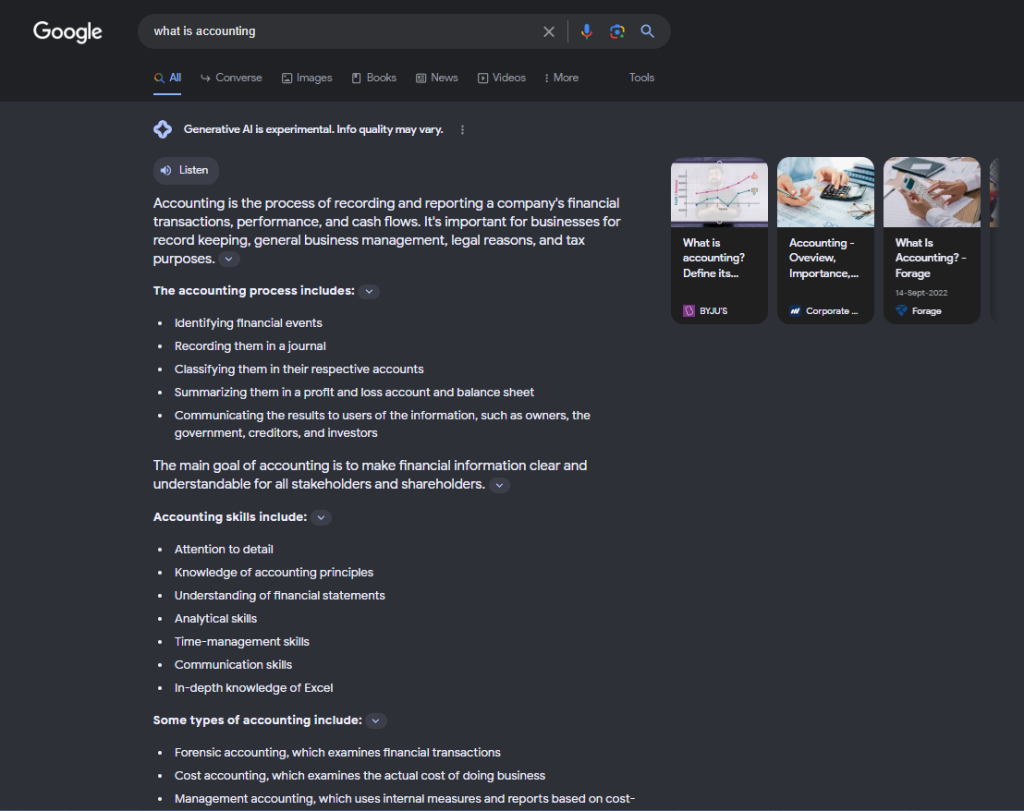
However, relying heavily on glossary terms and lightweight content in your SEO strategy poses a risk of losing Google traffic. It’s advisable for your company to shift its focus towards content that presents opinions and a distinctive point of view, something AI struggles to replicate.
Why? Because users desire insights from credible sources. This explains why people incorporate “Reddit” into their searches—real perspectives from individuals often outshine a mere collection of facts.
So, to ensure your mid- and low-funnel content proves effective, it should be not only comprehensive and opinionated but also incorporate unique insights that go beyond mere factual responses.
If your content delves deep, offers unique perspectives, contains original data, integrates rich media, and features insights from consumers, employees, and real people, then you’re on the right track.
Maintaining Competitive Parity
Let’s shift our focus away from word count and instead concentrate on two important factors: knowledge acquisition and competitive parity. Maintaining a strong presence in search results and obtaining a high ranking requires this change in emphasis.
Let’s delve into these ideas.
The goal of competitive parity is to align your content with the search intent of your chosen keyword topic. Essentially, it should, at the very least, match the type of content that Google currently prioritizes for your search query.
Take, for example, cybersecurity advice for customers. When it comes to top-ranking content, Google tends to favor pieces that explain potential risks and offer effective solutions. There’s no need to delve into the extensive history of cybersecurity; keep your content current and relevant.
Now, let’s discuss knowledge acquisition. In 2018, Google filed a patent that highlighted a system for ranking websites based on the originality of their content. Always keep the acquisition of valuable information in mind as you evaluate word count and research your competitors’ content. Using it as a benchmark enables us to consistently deliver value to our users, enhancing the quality of our content and increasing its potential for higher rankings.
So, why is this significant? Because both of these concepts work in harmony with Google’s strategy for providing helpful content. This approach promotes high-quality content that genuinely benefits readers. It significantly influences the performance of content in Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
We are organically creating content that aligns with Google’s principles by shifting our focus from word count to competitive parity and knowledge acquisition. This, in turn, ensures long-term search visibility and a higher ranking.
Monitoring And Adapting To SGE Updates
To properly comprehend the evolving landscape of SGE (Search Engine) trends, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of continuous monitoring and adaptation. Given the ever-changing dynamics, it becomes essential to employ analytics and SEO tools to assess performance and identify areas for improvement. Here’s how to integrate these vital components into your content strategy:
- Optimize your content by repurposing it for various channels, taking into account the evolution of SGE trends. Despite your best efforts, it’s important to anticipate a decrease in organic traffic as Google gives priority to displaying direct answers at the top of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). Recognizing the significance of staying attuned to these changes, you must adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Utilize analytics and SEO tools to monitor performance as part of this adaptive strategy. Regardless of how Google’s algorithms evolve, the primary objective remains enhancing the quality and value of your content. When it comes to repurposing your content, consider the following effective methods:
- Combine related blog posts to create high-quality ebooks, which you can distribute through various channels, including your website, email newsletters, and social media. This approach has proven to be beneficial, as evidenced by our SEO Content guide.
- Transform your blog posts into short videos for social media or engaging podcasts. Recognize that different audience segments have distinct preferences—some prefer videos, some favor podcasts, and some enjoy both. By repurposing your written content in these ways, you offer multiple avenues for audience engagement.
- Generate long-form social media posts and carousels using content from your blog. This is an excellent method to make the most of the content you’ve invested significant time and effort in creating.
- While AI appears to be driving these advancements, it can also serve as a valuable tool to support your content strategy in this rapidly changing market. For instance, ChatGPT can assist you in rewriting your content, generating scripts from existing pieces, summarizing content for social media posts, and more. Explore ChatGPT content prompts for useful assistance.
- Several other AI technologies can aid in creating videos and images. However, it is imperative to ensure that any content you publish meets the AI quality standards, taking into consideration factors like accuracy, usefulness, and human editing.
In summary, it is crucial to remain adaptable and well-informed in response to the ever-shifting SGE trends. Leveraging analytics and SEO tools to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement can help you maintain a competitive edge in the digital realm while making the most of content repurposing strategies.
Presenting Raggle: An SGE Proof Of Concept
When SGE was initially unveiled at Google I/O, there was a lot of excitement. However, it wasn’t made public until a few weeks later, which prompted the creation of a personal version to begin. Concurrently, a trial of the AvesAPI, a JSON SERP data source, became available.
The discovery that AvesAPI’s service could be used with Llama Index, an open-source framework for LLM applications, accelerated the development of a prototype matching SGE capability. This project, known as Raggle, can be found here.
To set the right expectations, it’s important to understand Raggle’s limitations. It was developed for research purposes and didn’t have the resources of a large team of engineers and PhDs. Here are the identified flaws:
- Response time is noticeably slow.
- Responsiveness is limited.
- Raggle provides only informative responses.
- It doesn’t generate follow-up queries.
- It relies on available AvesAPI credits; new queries won’t work if credits are exhausted.
Despite these limitations, Raggle has additional features and hidden components that help in understanding how Google uses RAG.
How Raggle Works
Raggle is essentially a RAG implementation of the SERP API. It sends the user’s query to AvesAPI during runtime to obtain the SERP. We promptly display the SERP HTML to the user and then crawl the top 20 results.
We store the extracted content from each page in the Llama Index, along with URLs, page names, meta descriptions, and og:images as metadata for each entry. The index is then queried using a prompt that combines the user’s original query with an instruction to respond in 150 words. To create the AI snapshot, we extract the best chunks from the vector index, attach them to the query, and submit it to the GPT 3.5 Turbo API.
The process of creating the index and querying it involves just three steps, which are easy to manage.
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = CitationQueryEngine.from_args
(
index,
# here we can control how many citation sources
similarity_top_k=5,
# here we can control how granular citation sources are, the default is 512
citation_chunk_size=155,
)
response = query_engine.query(“Answer the following query in 150 words: ” + query)
We use the citation methods provided by Llama Index to retrieve text blocks and their metadata for citation purposes, similar to how SGE operates.
finalResponse[“citations”].append
({
‘url’: citation.node.metadata.get(‘url’, ‘N/A’),
‘image’: citation.node.metadata.get(‘image’, ‘N/A’),
‘title’: citation.node.metadata.get(‘title’, ‘N/A’),
‘description’: citation.node.metadata.get(‘description’, ‘N/A’),
‘text’: citation.node.get_text() if hasattr(citation.node, ‘get_text’) else
‘N/A’,
‘favicon’: citation.node.metadata.get(‘favicon’, ‘N/A’),
‘sitename’ : citation.node.metadata.get(‘sitename’, ‘N/A’),
})
Feel free to explore it. You can visit the chunk explorer and examine the chunks used to inform the AI snapshot answer by clicking the three dots on the right. In this proof-of-concept, you’ll notice that the relevance calculation corresponds to the order of results displayed in the carousels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this post emphasizes the dynamic nature of SEO in the SGE era. The search landscape is constantly evolving due to the emergence of Google’s Search Generative Experience, and it falls upon digital marketers and SEO specialists to adapt and stay ahead.
The key takeaway is clear: stay well-informed, embrace change, and consistently enhance your SEO strategy. By doing so, you not only ensure your relevance in the ever-changing world of search but also position yourself for success in today’s and tomorrow’s competitive digital landscape. Adopting this approach is crucial for realizing the full potential of SEO and establishing long-term success in the SGE era.
FAQs
What impact does Google’s Search Generative Experience have on SEO strategies?
Google’s Search Generative Experience places a strong emphasis on user intent, context, and relevance. Therefore, SEO strategies need to prioritize providing high-quality and valuable content that aligns with user demands, all while acknowledging the dynamic nature of search algorithms.
Is keyword research still effective in the era of Search Generative Experience?
Absolutely, keyword research remains a fundamental aspect of SEO. However, it should be complemented by a deeper understanding of user intent. Given the conversational nature of contemporary search queries, it’s advisable to concentrate on long-tail keywords and natural language.
What role does user experience (UX) play in the Search Generative Experience?
User experience is pivotal. Google favors websites that offer a smooth and enjoyable user experience. To enhance your site’s visibility in search results, ensure fast loading times, mobile optimization, and user-friendly navigation.
Is the significance of backlinks still relevant in the context of the Search Generative Experience?
Backlinks continue to hold importance, but the focus has shifted from quantity to quality. High-quality and relevant backlinks from authoritative sources substantially contribute to a website’s trustworthiness and ranking in the Search Generative Experience.