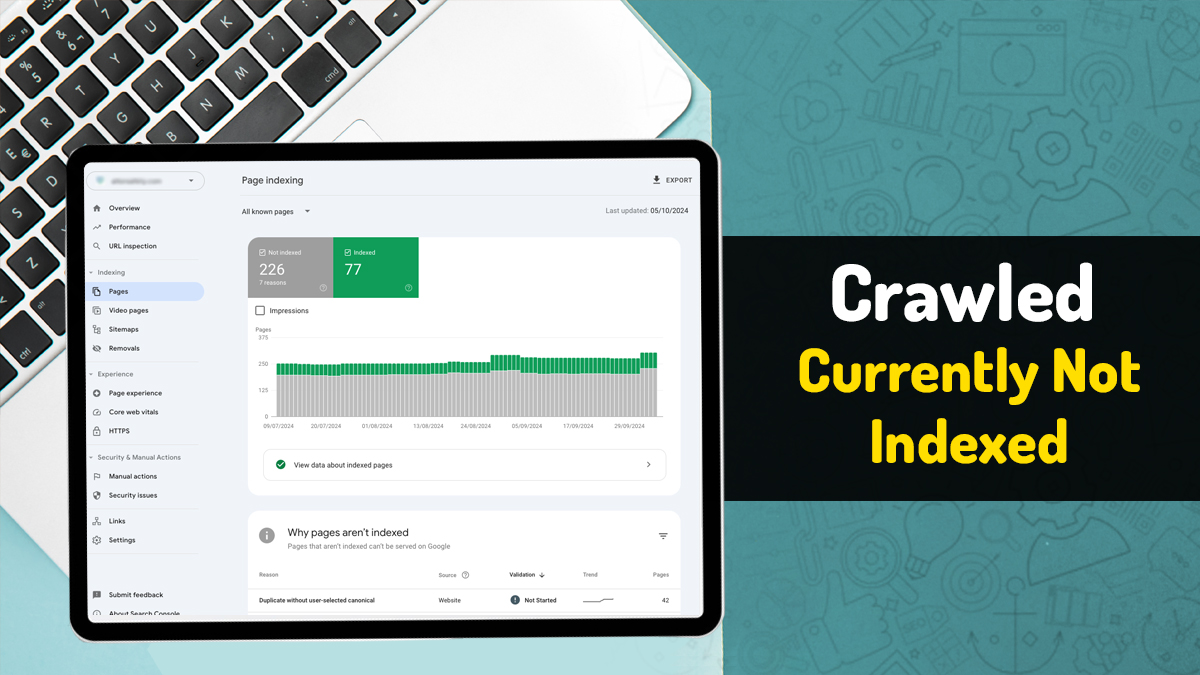
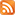The status “Crawled – currently not indexed” is a common notification in SEO management. It means that search engine bots have crawled a webpage but decided not to add it to their list of searchable pages. Google doesn’t explain exactly why a page gets this status.
It’s important for website owners to understand this status because it shows where they can make their website’s SEO better. Website managers can make specific changes to improve the content, use better keywords, and increase the chances of being seen in search results.
We know that pages often get this status when Google thinks they aren’t good enough to be listed. In this post, we will explain how to fix ‘Crawled – currently not indexed’ error in Google Search Console and increase the chances of a page appearing in search results.
What Does “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
The “crawled – currently not indexed” status in your Google Search Console means that Google has examined your webpage, but decided not to list it in its search results. This means that this page will not appear in Google search results for any search.
SEO services assist in resolving the ‘Crawled – Currently Not Indexed’ error by enhancing website performance, optimizing content, and ensuring proper technical SEO practices for improved indexing and visibility.
How to Fix “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed”?
It’s important to note that the “Crawled – currently not indexed” error is a bit different from the “Excluded by ‘Noindex’ Tag” error that you might also find in your Google Search Console indexing report.
Both have been crawled by search engines but not listed in search results. The “Crawled – currently not indexed” error can mean different things. Here is a list of common problems and some possible solutions to help Google index them.
Optimize Internal Linking
Google may not index a page if your website has a bad internal linking or doesn’t have any internal links. A page that has no links to it is called an orphan page. To fix orphan pages or make your internal linking better, go to a page on your site, find a part of the article that relates to the topic you want Google to recognize, and add a link to it.
You can find ways to link to your pages by searching on Google for the keyword that the orphan page is meant to target. You can search in Google like this:
Website:yourdomain.com “target keyword for orphan page”
The search results will show pages from your website that already have the keyword you are looking for and might give chances for linking to other pages. Internal linking is really important, so don’t overlook it. This idea only takes a few minutes and shows that the page is useful.
Low-Quality or Thin Content
Pages that have very few words might not have enough information and can be seen as thin content by Google. If that’s true, they might visit the page but not show it in the search results. Thin content occurs when your page has a lot fewer words than other top pages.
For instance, if all the search results have detailed information with over 3000 words, your page that only has a few hundred words might be seen as lacking in content. But if the top pages show different results and have different lengths, your page with hundreds of words might not have a problem with thin content.
To fix thin content, you should add more information to the page. Make the page long enough to fully explain the topic, but don’t make it too long. If you write a clear and useful article, Google will give it a good ranking.
Google won’t let you know if a page has little or poor-quality content. Instead, you should look at the search results and decide for yourself.
Search Intent
Another reason for pages saying “Crawled – currently not indexed” could be that the search goal doesn’t match what the page is about. This means there is a difference between what you have and what shows up in search results.
Here’s an example of how search intent affects search results for the question “how to calculate home loan interest?” This question is for information, and there are different types of results.
These include interest calculators, videos, and articles that explain how to do things. When you focus on this question, you may do well with various types of content. When looking for a “interest calculator,” you’re more likely to get better results with a calculator tool instead of a “how-to” article.
To make sure you understand what people are looking for, look at the pages that are at the top of Google before you create your content. To fix the problem of pages being crawled but not indexed because they don’t match what users are looking for, you need to change or rewrite the content on those pages.
Duplicate Content
Google tries to use its resources and crawling budget wisely. Google really dislikes content that is copied. John Mueller said that having duplicate content won’t get you punished, but it also doesn’t guarantee that Google will include the site in the search results.
They actually don’t want to include duplicate content. What will Google do if it thinks one of your website pages is a copy. Most likely, it will mark the page as “Crawled – currently not indexed”. Here are some situations where duplicate content might appear:
- Online stores that sell the same product in different styles or options, along with brief descriptions of each item.
- Websites with a lot of content made by users.
- Pages on a website that talk about the same or similar subject.
Google wants to skip adding copies of the same page from a website to make things better for users. This causes Google to remove some results. We suggest you look at the Performance report to find out which pages are already showing up for the search term you want your page to rank for.
When pages are about the same topic, you might want to add a canonical tag. This tells Google to only keep one of them in its index. This tag lets Google know which page is the most important and which one you want it to list. They usually follow canonical tags.
If the pages are not alike or you don’t want to use a canonical tag, think about changing the content on one of the pages.
Mismatch in Structured Data
Structured data helps bots of search engines understand what a web page is about. You can see how your structured data is doing in the Enhancements tab of your Google Search Console.
It’s very important to keep an eye on your structured data because errors can sometimes make Google not want to list your page, even if it has already crawled it. One example of this is product pages.
Mistakes in structured data can make Google misunderstand your page. This could lead to your page not showing in rich snippets and possibly not appearing in Google’s search results at all. Warnings are a bit different because they might still let your page be listed, but it may not appear in rich snippets.
Out of Stock Products
A common issue we often notice on online shopping websites is that some product pages show an error saying they are not indexed. This usually happens with pages that feature products that are out of stock or unavailable.
When Googlebot visits a URL, it looks to see if the product is available. If the product is not available, it marks it as crawled but not indexed. It makes sense for Google to do this because they care a lot about how users feel when using their service.
They don’t want links to appear if the products are not available. If you have an online store and see the “crawled – currently not indexed” error on your product pages, check your stock feed to make sure all available products are displayed on the page. You can then ask Google to crawl your web pages again.
Also Read: Product Page SEO: The Missing Link in Your E-commerce Strategy
301 Redirects
These are a way to automatically send someone from one web page to another. This happens when a page has moved to a different address. It helps keep links working and directs visitors to the right place.
Although this is an uncommon problem, especially on bigger and more trusted websites where links are crawled quickly and often, it can still happen. Sometimes, we notice the destination links of redirected pages appearing in the report for pages that are crawled but not indexed.
This isn’t about redirects being done wrong; it’s more about how often Google crawls your website. Sometimes, we notice that Google crawls a website but doesn’t add it to its search results. You can see this by looking at the search results page.
A simple way to solve this is to create a temporary sitemap.xml. Collect all the URLs from the report that lists pages not being indexed. Then, match these URLs with the redirects you have set up in Excel or Google Sheets. After that, create a sitemap using Screaming Frog and upload it to the Google Search Console.
Also Read: Right way to use 301 and 302 redirects
Private Information
Sometimes, Googlebot can see content that it shouldn’t be able to see. You might see an error message saying “crawled – currently not indexed” on these private URLs. Private pages are examples like development areas, pages that are only accessible for authorized personnel, and paid content, among others.
This can happen if Google isn’t checking your website carefully. Googlebot will explore every place it can to find helpful information for users. Use a tool like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to scan your website. Make a list of pages that should not be scanned. You can then choose what to do next.
This could mean taking away all links to these pages and deleting them from the sitemap, so Googlebot can’t find the page at all. Or you might need to make some changes to your robots.txt file to prevent Googlebot from looking at these parts of your website completely.
Other Factors
False Positive
A false positive happens when Google Search Console says a page is not included, but when you check it with the URL inspection tool or test it live, it shows that your page is actually included.
This situation is called a false positive in Google Search Console coverage. To run a live URL test:
- Visit Google.com and enter your webpage URL in the search box. For example, “domain.com/blog-post”.
- Then check the results and find your page URL.
If your page shows up in search results, it is indexed. This can happen even if Google Search Console says the page is excluded. This is what we call a false positive. You don’t need to do anything because this is just a mistake in the Search Console report.
Paginated URLs
Blogs and online stores use pagination to organize their content and make it easier to find what you’re looking for. Paginated URLs are web pages that have a number at the end to show the page, like domain.com/blog/5.
Google might choose not to include these pages in its search results. Whether you choose to fix the problem with pagination URLs depends on whether you think they are useful for search results. Will the paginated URL show up in search results? Take a look at Google’s tips for pagination.
RSS Feed
RSS feeds are useful for sharing content, but the links aren’t designed for people to read because they don’t have any formatting. If Google looks at your RSS feeds but doesn’t index them, it’s okay and you don’t need to be concerned.
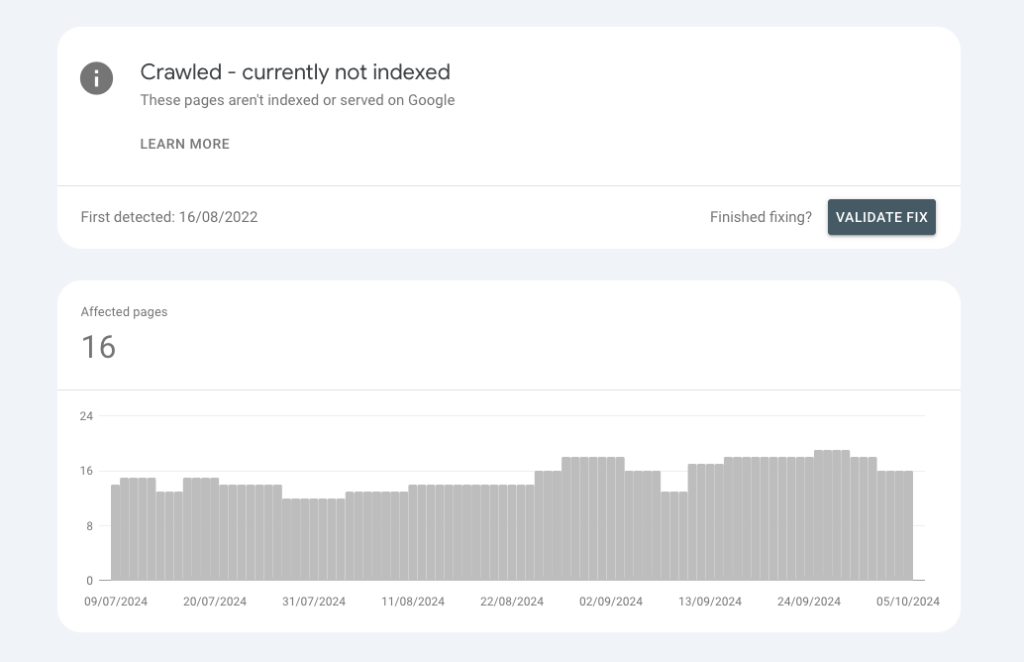
Difference Between “Crawled – Currently not Indexed” and “Discovered – Currently not Indexed”
Even though these two statuses seem very alike, there is one major difference. When a URL says “Crawled – currently not indexed,” it means that search engine bots have looked at the page but chose not to add it to their index.
This can happen for different reasons, like the content being poor quality, copied from somewhere else, or not having enough relevant links to it. Basically, the search engine found the page, but it didn’t meet the requirements to be included in search results.
“Discovered – currently not indexed” means that the search engine has found the URL in ways other than directly visiting the page. This could be through links on other pages that are already indexed or from submitted sitemaps.
But it hasn’t been crawled or listed yet. This status means the page might need some improvements or a better plan to help it get found and listed by search engines.
Both terms mean the page is not indexed. “Crawled” means the page was examined, while “Discovered” means the URL was found but not crawled yet. Knowing these details can help plan better ways to show up in search results.
To Conclude
The status “Crawled – currently not indexed” is important for webmasters who want to make their site more visible on search engines. When a web page has been visited by a search engine but is not stored in its index, it shows there might be problems to fix.
These could be related to the content quality, how relevant it is, or technical issues like the way the website is organized. By looking into why this is happening, website owners can create specific plans to improve their content and SEO efforts.
This might include improving how we use keywords, removing duplicate content, or getting more backlinks. It’s important to understand and fix the “Crawled – currently not indexed” status to help a website perform better. This way, search engines can find and rank important content properly.
FAQs
How can I find out if my page is being crawled or indexed by search engines?
You can easily see if your pages are being indexed by Google using Google Search Console. In the tool, you can go to the “Coverage” report to check which pages are included in search results, which are not, and their status. Also, the site search feature in Google will help you to easily check if a certain page is indexed in Google.
How can I get my crawled page to be indexed?
To help with indexing, begin by making your content better, make sure it’s helpful, original, and important for the people you want to reach. Optimize your SEO by finding the right keywords and tags. Also, get links to your page from well-respected websites. This shows bots of search engines that your content is important. After you make changes, you can ask Google Search Console to crawl your site again.
Does “Crawled – currently not indexed” impact my SEO?
Yes, this status can greatly affect how well your site ranks on search engines. Pages that aren’t indexed won’t appear in search results, so they won’t get any natural visitors. This can make it harder for people to find your site and may hurt your position for important keywords. To keep a good SEO profile, it’s important to find out why some important pages have a low score and fix any issues.
Should I get rid of pages that were crawled but not indexed?
You don’t always need to delete pages that have been crawled but are not in the index. Before deciding, check why something is not indexed. If the page could be useful, think about making its content better or improving its search engine practices. If the page is really low quality or old, it might be a good idea to take it down or send visitors to a better page to help improve the overall quality of the site.
Why does Google crawl a page but not index it?
Google may crawl a page but not index it due to factors like noindex meta tags, low-quality or duplicate content, or technical issues. Pages blocked by robots.txt or deemed irrelevant may also remain unindexed. Ensuring high-quality, original content, proper meta tags, and resolving technical issues can improve indexation.
What does it mean when something is not indexed?
When something is not indexed, it means that it hasn’t been included in the database of a search engine like Google, making it unavailable for search engine users to find through queries.
What is the difference between discovered currently not indexed and crawled?
The difference lies in the stage of the indexing process. Discovered – Currently Not Indexed indicates Google has found the page but hasn’t indexed it yet, possibly due to various reasons like low quality or duplicate content. Crawled means Google has accessed the page’s content, but it doesn’t necessarily imply indexing; it’s merely the first step in the process.
How do I fix Crawled – Currently Not Indexed?
To fix Crawled – Currently Not Indexed, follow these steps: Check robots.txt for crawler blocks, review meta tags for noindex, ensure high-quality, original content, submit an XML sitemap, use Fetch as Google tool, optimize internal linking, improve page load speed and mobile-friendliness, check for server issues, and be patient for indexing updates.