Google Cache is a database of all the websites that Google’s crawler bots have scanned and indexed. It’s a snapshot of a website’s content that Google takes at a particular time. For example, if a website is updated frequently, Google will crawl it more often, meaning the cached version will also be updated regularly. As a result, website owners and developers can use Google Cache to quickly access a snapshot of their website’s content as it appeared to Google at a specific time.
Google Cache is helpful for users having trouble accessing a website. Users may frequently view a cached website version using Google Cache even if it is unavailable or has technical issues. We will provide step-by-step instructions and practical tips for using Google Cache. Whether you’re a website owner, digital marketer, or curious about how Google Cache works, read on to learn more about this valuable tool.
Does Caching Improves SEO?
Google Cache is helpful for SEO as it allows you to see how Google sees and caches your website’s pages, which can help you identify technical issues and improve your website’s performance. Additionally, Google Cache can be used to recover lost or deleted content, which can help maintain your website’s search engine ranking and prevent traffic loss.
SEO services use Google Cache to recover lost or deleted content, which can help maintain a website’s search engine ranking and prevent traffic loss.
What Exactly Is Google Cache?
Google Cache is the HTML backup of the webpages reviewed and indexed by Google’s crawler bots. It saves a snapshot of a website’s content at a time. This is useful for website owners and developers who want to access an older version of their site or test their website. Users may also use Google Cache to access a cached version of a website if the site is down or experiencing technical difficulties.
All of the websites we can visit are hosted on remote servers. Therefore, Googlebot must visit websites, crawl through their material, and index them to offer search results to users.
Google takes an HTML snapshot of every webpage and saves it as a backup in case the live page is unavailable for any of the above reasons. Google Cache is a centralized database that stores millions of web pages as a backup.
The procedure enhances the user experience. For example, if any search results pique your attention but are not now available (due to being removed, unavailable, or whatever), you can visit the web page using Google Cache.
If you check Google search result pages, you’ll notice that the search results include pictures of the websites linked to them in the SERPS. This is because Google’s infrastructure tunes the algorithm in such a way that the search results with connections to relevant pages in Google Cache. This is remarkable because the caching mechanism is distinct from the crawling and indexing algorithms.
For example, if you type in what it is in Google Cache, you will obtain around 76,90,00,000 results, each containing a link to a live website and a page in Google Cache.
Google continuously updates Google Cache. If a designer modifies a website, the changes will only appear in the Google Cache once Google updates the website snapshot.
How does Google Cache work
Google Cache is a database that stores a snapshot of a website’s content at a specific time. Google’s crawler bots scan and index websites and the cached version of a website is created when Google takes a snapshot of its content.
The cached version will be updated if a website is updated frequently. In addition, website owners and developers can use Google Cache to access a snapshot of their website’s content at a specific time.
Additionally, if a website is down or experiencing technical difficulties, users can often access a cached version of the site through Google Cache.
Overall, Google Cache is a valuable tool for website owners, developers, and users who need to access a snapshot of a website’s content quickly and easily.
Also, Read: What is cloaking in SEO? And Permitted Cloaking Practices
Why Is Caching Necessary?
Web page caching refers to temporarily storing a copy of a web page’s content in a cache, typically on the user’s local device or an intermediary server. Caching can significantly improve website performance by reducing page load times, improving server response times, and reducing network congestion. Here are some reasons why web page caching is necessary:
Faster page load times
One of the primary reasons for caching web pages is to reduce page load times. When a user visits a website, their browser sends a request to the server to retrieve the web page’s content. This process can take several seconds, mainly if the web page contains large images, videos, or other multimedia content. However, if the web page is already cached, the browser can retrieve the content from the cache instead of requesting it from the server, resulting in much faster load times.
Improved server response times
Caching web pages can also improve server response times. When a website receives a large number of requests, particularly during peak traffic periods, the server can become overloaded, leading to slow response times or even server crashes. However, if the web pages are cached, the server can serve the cached content to users, reducing the load on the server and improving response times.
Reduced network congestion
Web page caching can also help to reduce network congestion. When a user visits a website, their browser sends a request to the server for the web page’s content. This request travels over the internet, and if the user is located far away from the server, it can take a long time for the bid to reach the server and for the content to be delivered back to the user. However, if the web page is cached, the content can be provided from a local cache, reducing the amount of traffic on the internet and improving overall network performance.
Improved user experience
Caching web pages can significantly improve the user experience by reducing page load times and improving server response times. When web pages load quickly and respond promptly, users are more likely to stay on the site and engage with its content. Conversely, slow-loading pages and unresponsive servers can frustrate users and drive them away from the site.
Better search engine rankings
Web page caching can also help to improve a website’s search engine rankings. Google, for example, uses page speed as a ranking factor in its search algorithm, so websites that load quickly are more likely to rank higher in search results. By caching web pages, websites can improve their page speed and increase their chances of ranking higher in search results.
Reduced server load
Caching web pages can also reduce the load on servers. When a web page is requested, the server must process the request and generate a response, which can consume a significant amount of server resources. However, if the web page is already cached, the server can simply serve the cached content, reducing the load on the server and improving its overall performance.
In short, web page caching is essential for improving website performance, reducing page load times, improving server response times, reducing network congestion, and providing a better user experience. In addition, by caching web pages, websites can improve their search engine rankings, reduce server load, and ultimately increase their overall success.
Also, Read: How to Create Snippet Worthy Content for SERP Features
When Should You Use Google Cache?
There is a time and a place for everything. Therefore it’s essential to understand when to use Google Cache. Here are a few examples of when you’ll need to accomplish this.
Viewing Geo-Restricted Content
Geo-restrictions are frequently on websites for several reasons. First, Google Cache has no bounds. Users may access their favorite web material using Google Cache even if the original website is unavailable. If you are in this situation, you may easily overcome geo-restrictions using Google Cache.
Scanning the Latest Crawling Dates
Your content efforts will be reflected in your website’s ranking on search engine result pages (SERPs). On the other hand, making changes to your website and adding fresh material only guarantees immediate results. This is because Google will have to re-index your website first. The only method to discover when Google last crawled your website is to utilize Google Cache. The Index Coverage report in Google Search Console provides precise information on when Google Search Console last scanned your sites and if they have previously been indexed.
However, changes that result in a rich snippet will not reflect how your website looks in SERP unless Google re-indexes your websites. So watch the last indexing dates to determine when your modifications will appear in SERPs.
Retrieving Missing Content
Content that needs to be recovered is stuff that has been removed. Google Cache makes it easy to access, which is excellent news for site owners and users. For example, if your hosting company fails to back up your website and it is erased due to a server problem or hack, you can restore it through Google Cache.
The same applies to users who realize their favorite website is no longer available. You may go back and explore your favorite stuff thanks to Google Cash, even if it is no longer available on the main website.
Accessing Cache-Filled Versions of a Website
It’s time to learn how to access cached versions of websites now that you know what Google Cache is, why it matters, and when to utilize it. There are various options, and we’ll walk you through each in detail.
Direct Access to Cached Websites Using Google
Here are the steps to access a website’s cached version through Google:
- First, enter the search term into Google’s search box.
- Make sure to add “www.websitename.com” to the search term if you want to find websites directly.
- Then, Google will display the search results page.
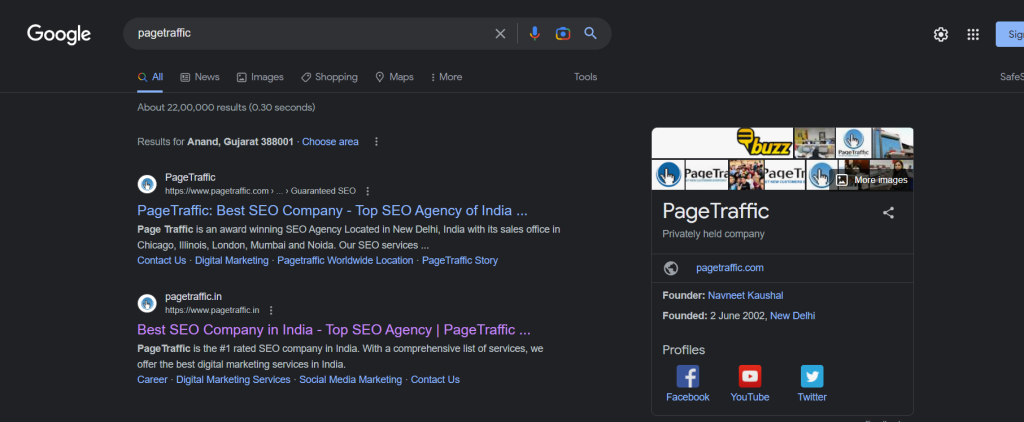
- Locate the website you are searching for in the search results.
- Next, click the three dots next to the website.
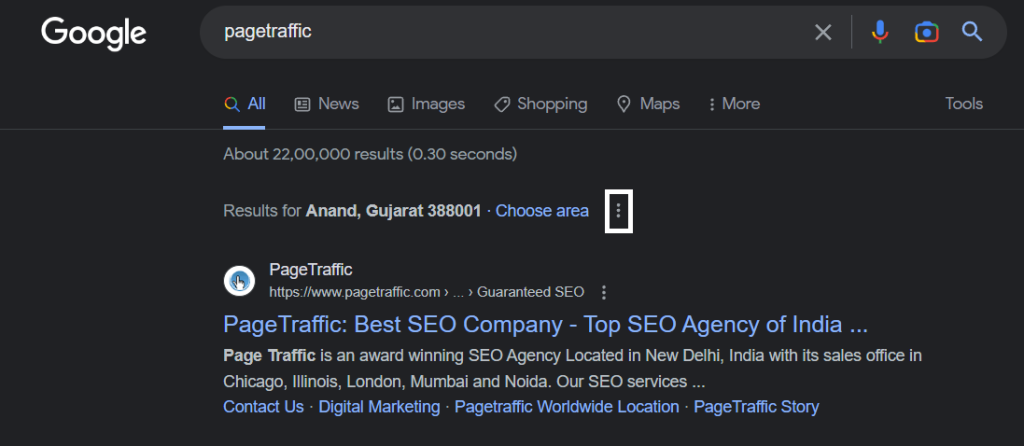
- Select “Cached” from the pop-up menu that appears.
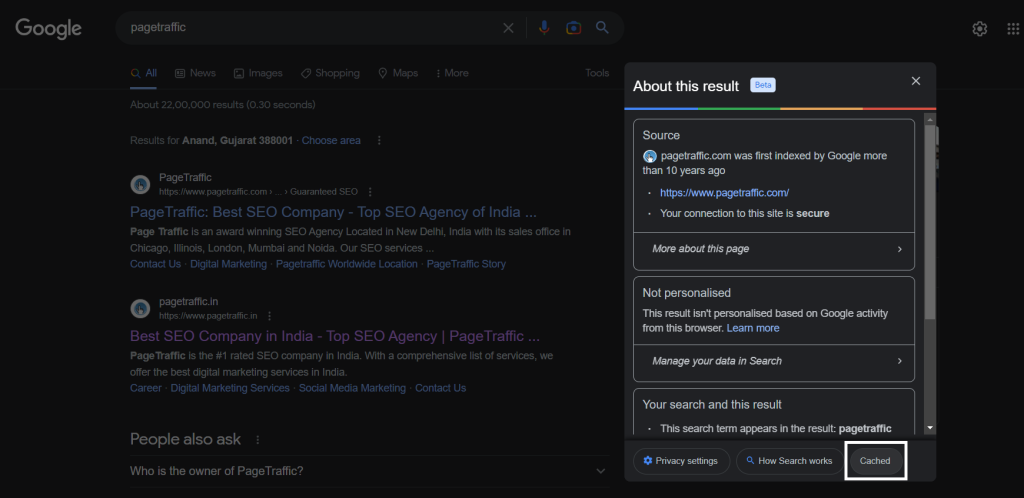
- Google will display the cached version of the website stored in its database.
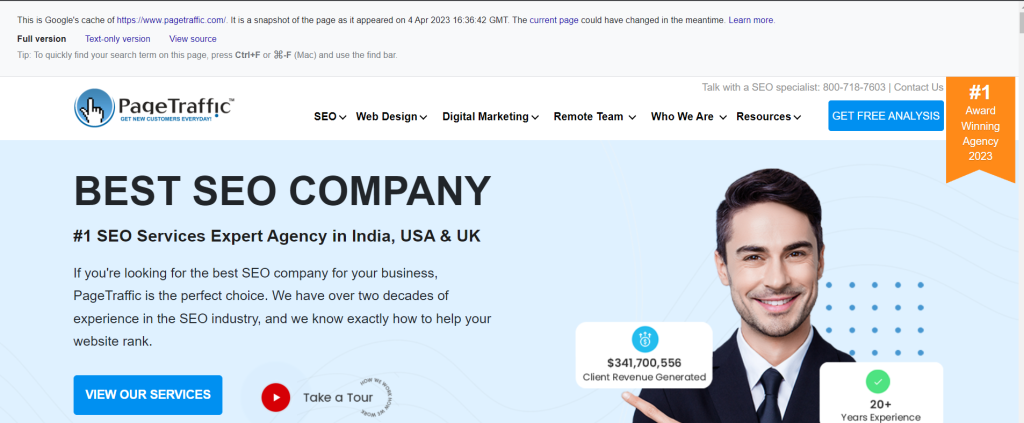
When you select Cached, Google will present you with the most recent version of the website that Googlebot has crawled.
You may select from the Whole version, Text-only version and See Source versions of a cached web page.
You may view a rendered version of the cached page by selecting the Full version. Although View source enables you to view the HTML code indexed by Googlebot, Text-only removes the CSS and shows the website without any pictures.
Use the Chrome Web Browser
Google Chrome’s web browser offers direct access to Google Cache. Launch Google Chrome and enter cache:www.websitename.com into the address bar.
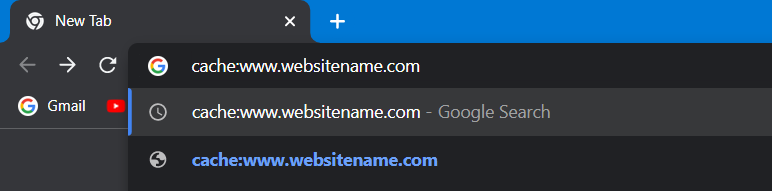
By performing this step, you may bypass the search results and go straight to cached copies of your favorite websites or your own website.
Use Google Chrome Extensions
Here are the steps to use the Web Cache Viewer Google Chrome extension to view cached versions of websites:
- First, add the Web Cache Viewer extension to Google Chrome.
- To do this, simply click “Add to Chrome.”
- Once the extension is installed, you can view cached versions of websites on the go.
- To view a cached website version, right-click anywhere on the page.
- Then, select “Web Cache Viewer” from the dropdown menu that appears.
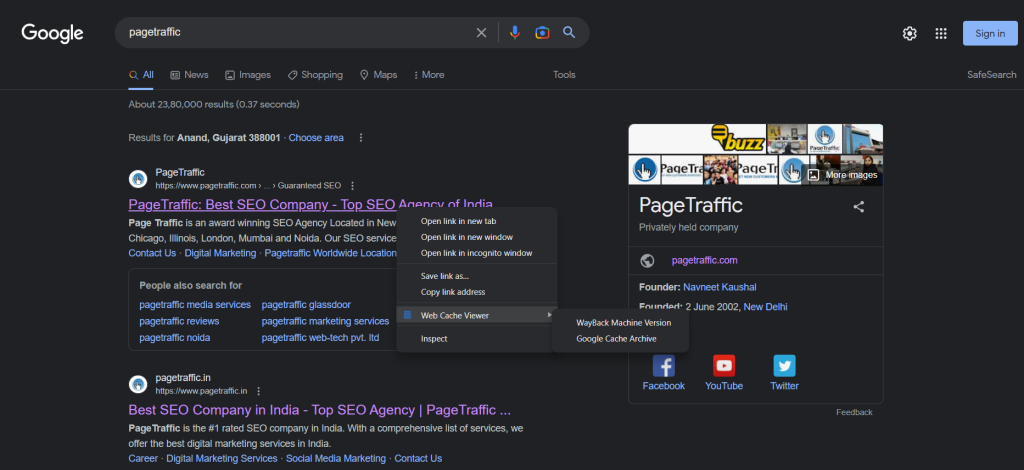
- Then, select “Google Cache Archive.”
- The Web Cache Viewer extension will then display the most recent version of the page that Google has indexed.
- You can use this feature to quickly access cached versions of websites while browsing on the go.
Investigate Various Web Archives
You might be surprised to learn that there are other organizations preserving web pages than Google. Across the world, other online archiving projects are now carrying out similar operations. Google might be less reliable than they regard updates and crawling, but it can still be helpful when trying to access material from geo-blocked or removed web pages.
We must mention only some online archiving projects, as many exist. Here are some further examples:
EU website archive
Wayback Machine on the Internet Archive
Term End Web Archive
Conclusion
A valuable tool to have at your disposal is Google Cache. You may utilize indexed pages as a backup for your website, get around geo-restrictions, recover deleted information, or manage your marketing, content, and SEO activities. As you can see, in addition to Google Cache, there are additional online archiving projects that you may employ.
FAQs
What is Google Cache, and how does it work?
Google Cache is a database that stores a snapshot of a website’s content at a specific time. Google’s crawler bots scan, index websites, and the cached version of a website is created when Google takes a snapshot of its content.
Why should I use Google Cache?
Website owners and developers can use Google Cache to access a snapshot of their website’s content at a specific time. For example, users can often access a cached version of a website if it is down or experiencing technical difficulties.
How do I access a website’s cached version through Google?
To access a website’s cached version through Google, enter the search term into Google’s search box, click the small gray arrow next to the website, and select “Cached” from the drop-down menu that appears.
Can I access Google Cache on the go?
Yes, you can use Google Chrome extensions such as Web Cache Viewer to view cached versions of websites on the go.
How frequently does Google update the cached version of a website?
The cached version will be updated if a website is updated frequently. Google’s crawler bots crawl frequently updated websites, meaning the cached version will also be updated more regularly.
Is Google Cache available for all websites?
Google Cache is only available for some websites, as some website owners may choose to prevent their websites from being cached by search engines.